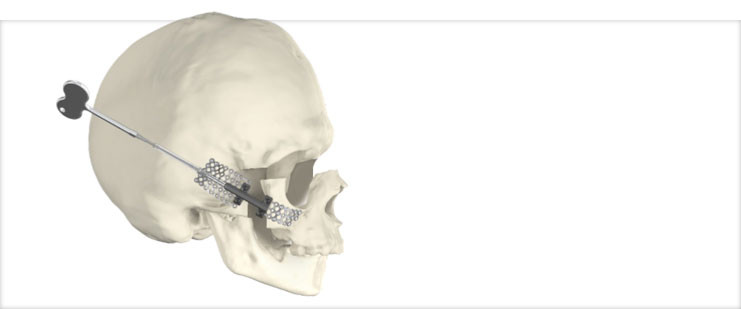
Advance MidFace Distractor
Overview
The Advance Midface Distractor is an internal distraction device that provides temporary stabilization and gradual lengthening of the cranium and midface. It is designed for the treatment of cranial and midfacial conditions where reconstructive osteotomy and segment advancement are indicated.
Features and benefits
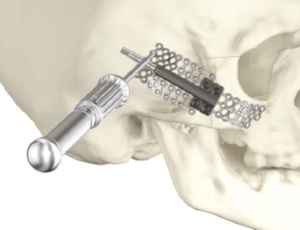
Modular system
A variety of plate designs are available to fit your patient’s anatomy and your surgical needs. All footplates are compatible with the 1.7mm Midface screws and instrumentation.

Type II Anodization
The device body and plates undergo Type II anodization, improving the surface finish. This finish may reduce the risk for tissue and bone adhesion, which can simplify the device removal.
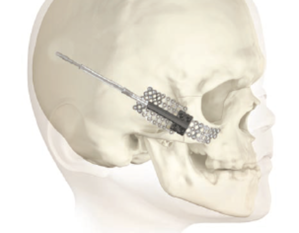
In-office removal
The activation rod can be removed within the office and out-patient settings. This may potentially eliminate the need for additional operating room time and cost.
Clinical evidence
BACKGROUND
Cephalocranial disproportion describes a state of volume mismatch between brain size and intracranial space. Nonsyndromic single-suture craniosynostosis patients can present with symptoms from elevated intracranial pressure because of inadequate or delayed treatment. The purpose of this study was to present five sagittal synostosis children with symptomatic cephalocranial disproportion treated with cranial vault distraction osteogenesis.
METHODS
Asymmetric transverse internal distraction osteogenesis was performed to preferentially expand the posterior cranium. A wider base plate, pivot screw, anterior hinge plate, and flexible drive rod were applied to minimize device failure while accomplishing lateral rotation of parietal bones. A distraction protocol was developed and produced consistent results.
RESULTS
Two girls and three boys underwent distraction for sagittal synostosis between 2002 and 2006. Average age at surgery was 5.8 years. All had resolution or amelioration of preoperative symptoms. Average operating room time for distractor placement was 2.5 hours (152 minutes) and average hospital stay was 2.8 days. The average distracted distance was 14.4 mm. Average operating room time for distractor removal was 1.1 hours (69 minutes) and average hospital stay was 1.6 days. No perioperative complications occurred. Average follow-up period was 4.2 years, with no recurrence of symptoms.
CONCLUSIONS
Symptomatic cephalocranial disproportion can present in older children with craniosynostosis. Asymmetric transverse distraction of the posterior cranial vault is a safe and effective treatment modality for this population.
CMF-WC-75_Rev. None_25719


