MEDPOR®
Plastic surgery
Overview
MEDPOR has been a trusted name in the industry since 1985, with hundreds of thousands of procedures performed, and hundreds of published clinical reports in reconstructive, cranial, oculoplastic, and cosmetic applications.
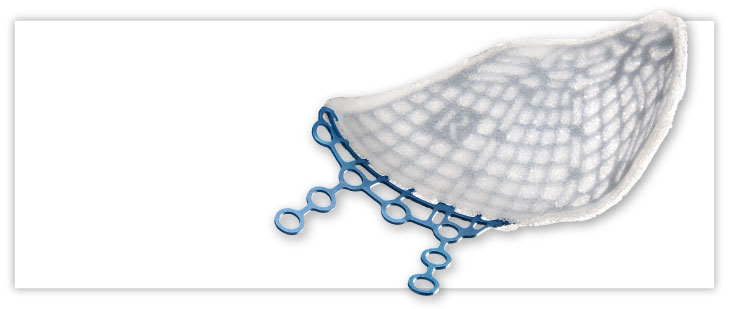
Our MEDPOR product line provides you an array of porous polyethylene solutions for your reconstruction and augmentation needs. We understand that bio-compatibility characteristics of implants are paramount to help surgeons achieve positive patient outcomes. The omni-directional pore structure of our polyethylene implants may increase implant acceptance by allowing the patient‘s native tissue to integrate with the implant. In addition to our comprehensive line of stock MEDPOR implants, we offer CT-based patient-specific implants, putting the implant design in your hands.
Proven. Adaptable. Comprehensive.
Features and benefits

Proven material
More than 400,000 procedures have been performed with MEDPOR Biomaterial, with more than 350 published clinical reports in cranial, reconstructive, oculoplastic and cosmetic applications.
Comprehensive portfolio
Wide variety of facial implants to fit patient and surgeon reconstructive and augmentation needs.

Adaptable
If desired, MEDPOR material may be cut and shaped to fit patient and surgeon needs.
Sterile
Implants packaged sterile and ready to use. They can be stored in the hospital or office to have on hand as needed.
Clinical evidence
The use of implantable biomaterials has become an integral part of aesthetic and reconstructive surgery of the face. Metals are used for fracture fixation devices, whereas polymers are used primarily for bone or soft-tissue substitution. This review of the scientific literature examines the risks and complications of these materials. First, we present an overview of commonly used materials. Second, we address general considerations of toxicity relevant to all biomaterials. Third, we present data from a large number of clinical series on the incidence of complications for individual materials used in specific applications.
A novel approach to increase chin projection with alloplastic material is presented. Key aspects of the technique include the consideration of anthropometric normal values in preoperative assessment and planning, a submental approach with wide subperiosteal exposure of the area to be augmented, the use of two-piece porous polyethylene implants for augmentation, and screw fixation of the implant to the mandible. Screw fixation improves the predictability and precision of reconstruction by preventing implant displacement, by obliterating gaps between the implant and the facial skeleton, and by facilitating final implant contouring. In a series of 46 patients (24 primary and 22 secondary) operated on over a 6-year period, this approach allowed anatomically correct, stable chin contours to be created. Iatrogenic problems with macrogenia, mentalis dysfunction, and soft-tissue distortion resulting from implant migration and capsular contracture have been avoided. There have been no infections. Two patients who had had multiple previous chin operations requested revisional surgery to refine contour.
Ideal surgery for congenital microtia-atresia would offer excellent cosmetic and hearing rehabilitation, with minimal morbidity. Classic approaches require multiple procedures, including rib cartilage harvest and aural atresia repair. Our facial plastic and otologic team approach incorporates a high-density porous polyethylene (Medpor, Porex Surgical, Newnan, GA) auricular framework, followed by single-stage bone-anchored hearing aid (BAHA) implantation. We evaluated the efficacy, safety, and morbidity of this 2-stage dual system approach. A prospective database of microtia patients was used to identify patients undergoing combined Medpor/BAHA auricular reconstruction and hearing rehabilitation between 2003 and 2006. The first stage involves placement of a Medpor framework beneath a temporoparietal fascia flap, followed by a second-stage procedure for lobule transposition and BAHA implantation. Twenty-five patients (28 ears) were evaluated. Aesthetic quality of the implants was excellent, with a high degree of framework detail visible, and a postauricular crease created in all patients. All patients were satisfied with the cosmetic result. There were no major Medpor complications such as infection, extrusion, loss of implant, or flap necrosis, and a 10.7% incidence of minor complications requiring operative revision. BAHA significantly improved hearing in all patients, with a complication rate of 31.8%, mainly skin overgrowth and cellulitis. The Medpor/BAHA dual plastic-otologic approach to microtia-atresia has produced excellent cosmetic results and hearing outcomes, which compare favorably to traditional microtia-atresia repair. This is a 2-stage aesthetic and functional protocol with an acceptably low rate of complications, which safely and efficiently achieves both aesthetic and functional goals.
Ear reconstruction is a difficult procedure requiring a framework and soft tissue covering. The traditional method uses a rib cartilage framework placed beneath scalp skin. This method has been used for 50 years despite inherent problems with both harvesting rib cartilage and using scalp for coverage. The authors describe a method using a porous polyethylene (PPE) framework covered by a large temporoparietal fascia (TFP) flap raised with the underlying subgaleal fascia (SGF). The entire implant is covered by the two-layered flap, which can be raised without any scalp incision. The skin grafts applied to the covered implant lie on the SGF. The trilaminar structure of the SGF allows the skin to move independently over the implant, resisting shear forces and reducing the probability of implant exposure. Ear reconstruction using the PPE framework was performed on 786 ears over an 18-year period. Initial complications were common. With improved implant design and complete coverage of the implant with both the TPF and SGF, exposure rate dropped to 7% with a 12-year follow-up. Implant fractures decreased to less than 3%. The PPE/TPF method allows earlier ear reconstruction in children with minimal scarring and discomfort. The reconstructed ear can closely mimic the shape and projection of the natural contralateral ear in fewer stages and with a shorter learning curve.
Inadequate projection of the midface skeleton results in midface concavity. Patients with this skeletal morphology tend to have prominent eyes and noses. Lack of skeletal support for the midface soft tissue envelope predisposes to premature cheek descent, resulting in palpebral fissure distortion and lower lid "bags," an appearance of early aging. Concave midfaces can be made convex with two basic maneuvers performed through intraoral and periorbital incisions. Midface skeletal projection can be increased by augmenting the facial skeleton with alloplastic implants. Multiple implants are required to replicate the complex curvature of the midface skeleton and to avoid impingement on the infraorbital nerve. Subperiosteal elevation of the midface soft tissues and repositioning provides cheek fullness and narrows the palpebral fissure while masking eyelid "bags." The resultant midface concavity makes the eyes and nose appear less prominent. This procedure has been a safe and effective treatment for 14 patients treated over a 4-year period.
CMF-WC-55_Rev. None_18994








.jpg)